Introduction to Suspension Casters
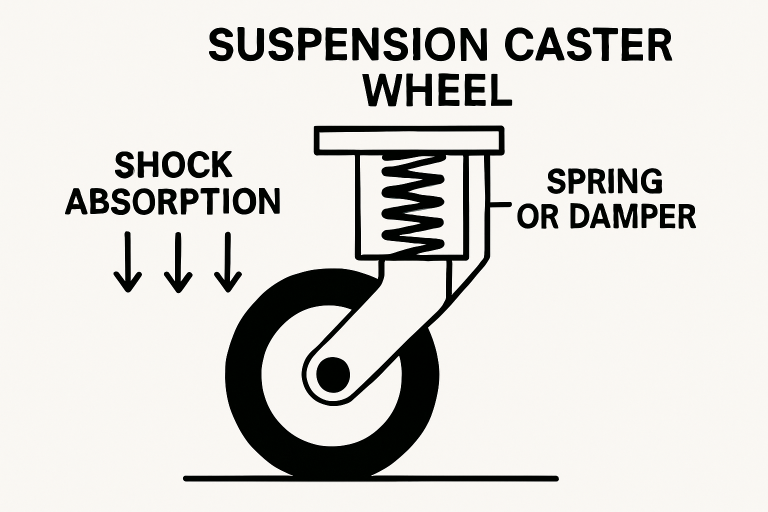
Modern material handling demands versatile equipment capable of transporting loads efficiently while minimizing the risk of damage to both the floors and the goods in motion. Suspension casters have emerged as a specialized solution for industries that value stability, protection, and performance. By integrating innovative suspension systems, these casters absorb shock and dampen vibrations, which is especially beneficial for environments where delicate or valuable items must be moved over irregular terrain.
Unlike conventional casters, suspension casters feature mechanisms that allow smooth, shock-free transportation, improving safety and better outcomes for sensitive equipment. The technology behind these casters protects the load and extends the life of floors and rolling stock by minimizing surface wear. Businesses in the healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics sectors rely on this advanced technology to ensure reliable mobility and asset protection.
How Suspension Casters Operate
The core advantage of suspension casters lies in their unique internal suspension mechanism. When encountering abrupt changes in floor elevation or minor debris, the caster’s suspension system compresses, dispersing the impact energy. This allows the caster to glide more evenly, reducing jostling or tipping and maintaining stability for heavy and light loads. This continuous adaptation to surface irregularities protects sensitive equipment and offers a quieter, more controlled movement, essential in hospitals and laboratories.
The effectiveness of these casters depends on precision engineering. The integrated shock-absorbing elements—often elastomer springs or hydraulic dampers—ensure that each wheel operates independently, adjusting to variable pressure and obstacles. This level of sophistication enhances user safety by reducing manual strain and guards against unexpected failures due to excessive vibration or impact.
Key Features of Suspension Casters
- Shock Absorption: Advanced internal mechanisms soak up impact and help prevent damage to fragile items.
- Vibration Reduction: Significantly lowers operational vibration, improving caster and load lifespan.
- Enhanced Mobility: Facilitates effortless navigation across thresholds, expansion joints, and rough surfaces.
- Floor Protection: Softens the effect of heavy rolling loads, minimizing scratches and floor wear in high-traffic areas.
Comparing Suspension Casters to Spring-Loaded Casters
While suspension and spring-loaded casters are engineered to manage shocks and vibrations, their design differences affect their performance in demanding environments. Suspension casters use sophisticated, independent suspension systems that provide superior vibration isolation and load stability. In contrast, spring-loaded casters depend on simpler spring mechanisms that can be less effective on continuously uneven terrain or during repeated impacts. The comprehensive damping abilities of suspension casters lead to safer movement for sensitive or valuable loads, making them the choice for applications where reliability and load integrity are paramount.
Applications of Suspension Casters
The versatility and resilience of suspension casters make them indispensable in a diverse range of industries:
- Medical Equipment: Smooth, quiet transit for hospital beds and clinical devices, vital for patient safety and equipment accuracy.
- Manufacturing: Enables the protection and precise movement of heavy tool cabinets and machine components in bustling workshops.
- Aerospace: Safeguards expensive, precision instruments and assemblies from disruptive shocks during floor transport.
- Food Service: Reduces fragile dishware and glass breakage by ensuring stable cart movement in fast-paced kitchen environments.
- Warehousing: Allows for the reliable movement of inventory and material-handling carts across uneven, high-traffic warehouse floors.
Choosing the Right Suspension Caster
Selecting optimal suspension casters requires careful consideration of specific application demands and environmental realities. Here are the core selection criteria:
- Load Capacity: Match caster capacity with the heaviest operational load, including the equipment and expected contents.
- Terrain: Determine the level of shock absorption needed by assessing the typical surfaces and obstacles encountered.
- Frequency of Use: Choose industrial-grade casters for continuous use, or lighter models for occasional or low-impact jobs.
- Environmental Conditions: Factor in moisture, chemical exposure, and temperature extremes to ensure caster longevity and dependability.
Maintenance and Longevity
Continued reliable performance from suspension casters depends on routine inspection and proper maintenance. Regularly check for signs of wear or corrosion, ensure the suspension mechanisms function smoothly, and clean the casters to remove debris that can impede movement or damage the internal components. Lubricating moving parts and promptly replacing damaged casters reduces the risk of equipment failure, bolstering workplace safety and efficiency.
Conclusion
Suspension casters represent a significant advancement in caster technology, providing businesses with enhanced mobility, superior shock absorption, and critical load protection. By understanding their functions and selection processes, facility managers can prioritize operational efficiency and equipment safety. Investing in the right suspension casters minimizes downtime, reduces replacement costs, and protects investments, offering long-term value across various industries. For a wider overview of the uses and benefits, consult industry publications and standards, as referenced above.