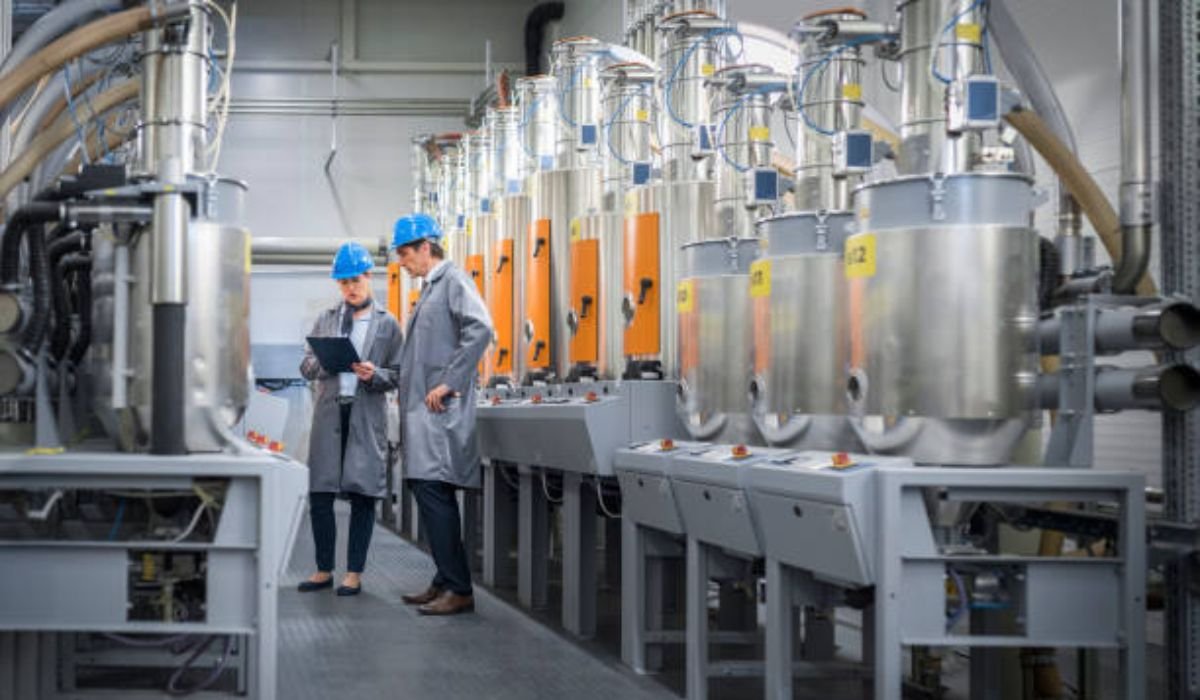
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing environment, chemical blending is no longer viewed as a simple passive function—it’s a strategic foundation for achieving optimal product quality, improving operational efficiency, and upholding stringent environmental standards. As industry leaders strive to outpace competitors and satisfy growing regulatory requirements, they are reimagining traditional approaches to blending to unlock new levels of control and flexibility. Innovative methods and equipment are propelling manufacturers toward higher yields and purer products, all while reducing costs and potential risks to both workers and communities. Selecting an industrial mixer for chemicals now involves much more than meeting simple blending requirements—modern manufacturers seek equipment that can integrate new technologies and support more sustainable operations, such as those that automate batch adjustments or reuse process heat for improved efficiency.
As global markets become increasingly competitive and regulatory demands intensify, adopting the latest chemical blending practices is crucial for achieving long-term success. From smart factories equipped with advanced digital systems to eco-friendly initiatives tackling some of today’s most urgent environmental challenges, the pathways forward are being reshaped by visionary thinking and collaborative innovation. Manufacturers who stay abreast of these emerging trends position themselves to respond rapidly to market changes, comply with new safety requirements, and capitalize on the growing demand for more sustainable and reliable chemical products.
Embracing Digital Transformation
Digitalization is revolutionizing chemical blending through the use of AI and IoT. Unlike traditional approaches that relied heavily on manual labor, modern digital solutions gather real-time data to enhance process optimization, predictive maintenance, and quality assurance. IoT sensors track variables such as temperature and pressure, minimizing downtime and preventing costly disruptions, especially in large-scale operations. Advanced factories utilize digital twins and remote monitoring to predict potential issues, optimize energy usage, minimize waste, and notify staff of any problems. These technologies facilitate process adjustments, boost productivity, and ensure safety compliance, ultimately strengthening customer trust and market position.
Advancements in Flow Chemistry
The transition from batch to flow chemistry signifies a major advancement in manufacturing. Flow chemistry, also known as continuous flow processing, involves conducting reactions in a continuous stream instead of in isolated batches. This method enhances control over parameters such as temperature, mixing, residence time, and pressure, resulting in improved product consistency and significantly reduced waste and reprocessing. It also reduces environmental impact and increases safety when handling hazardous or exothermic reactions, enabling safer scaling up of processes. Collaborations like those between Imperial College London and BASF highlight the industrial potential of flow chemistry. Overall, this progress yields high-throughput, energy-efficient processes, easier automation, digital integration, and compact, scalable units that are less costly than traditional plants.
Green Chemistry Initiatives
The push for greener and safer chemical manufacturing underscores the importance of green chemistry—developing processes that minimize the use of hazardous substances. It emphasizes sourcing renewable feedstocks, lowering solvent use, and improving energy efficiency. Many companies are transitioning from petroleum-based raw materials to sustainable alternatives, promoting a circular economy that reduces dependence on fossil fuels and lowers emissions. Green chemistry lessens environmental impact and operational risks, and can generate revenue through byproducts. These initiatives are driven by regulatory requirements, consumer demand, and potential cost savings. Designing safer processes helps avoid expensive cleanup and penalties.
Collaborative Innovations
The path to a smarter, more sustainable manufacturing future depends on collaboration among universities, industry leaders, and technology providers. Academic-industry partnerships translate research from labs into commercial applications. For instance, the consortium led by Imperial College London and BASF pools expertise and resources to innovate in flow chemistry, catalyst design, and process intensification. These collaborations address challenges such as reducing environmental impact, automating processes through robotics and machine learning, and developing eco-friendly catalysts and solvents. Collaborating with research organizations and equipment manufacturers enables companies to remain innovative, adapt quickly, and continually improve their operations. Such partnerships also generate joint intellectual property, train future scientists, and offer opportunities to pilot new technologies in manufacturing.
Conclusion
Innovations in chemical blending are redefining the manufacturing landscape, opening up exciting new possibilities for achieving higher yields, better quality, and lower emissions. By embracing digital transformation, advancing flow chemistry, promoting green initiatives, and fostering collaboration, the industry is charting a course towards operational excellence, ecological responsibility, and sustained competitive advantage. Companies willing to invest in and adapt to these innovations will be well-positioned to remain leaders in an ever-changing global market, delivering products that meet both high-performance benchmarks and modern sustainability requirements.